Kicking off with Stock Market Basics, get ready to dive into the fundamentals of how the stock market works and why it’s crucial in the economy. Buckle up for an exciting ride through the world of stocks and investments!
Stock Market Basics
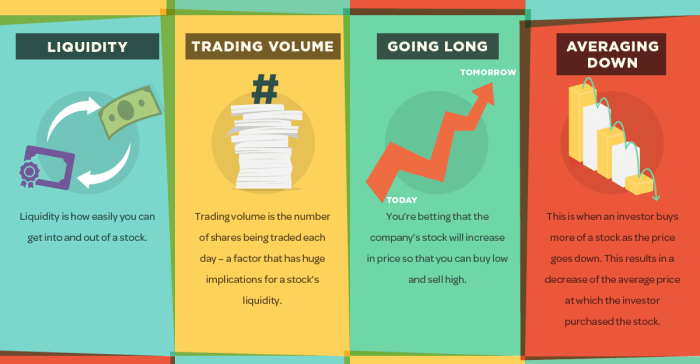
The stock market is a place where investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It functions as a marketplace where buyers and sellers come together to trade stocks, providing liquidity to investors.
Primary Participants in the Stock Market
The primary participants in the stock market include:
- Individual investors: People like you and me who buy and sell stocks through brokerage accounts.
- Institutional investors: Entities like mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds that invest large sums of money in the stock market.
- Stock exchanges: Platforms where stocks are traded, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ.
Importance of the Stock Market in the Economy
The stock market plays a crucial role in the economy by:
- Providing companies with a source of capital through initial public offerings (IPOs) and secondary offerings.
- Allowing investors to participate in the growth of businesses and share in their profits through capital appreciation and dividends.
- Facilitating the efficient allocation of resources by pricing assets based on supply and demand.
Types of Stocks
When it comes to investing in the stock market, it’s important to understand the different types of stocks available. Let’s dive into the various categories to help you make informed decisions.
Common Stocks vs. Preferred Stocks
Common stocks are the most commonly traded securities in the market. They give shareholders voting rights and the potential for dividends. On the other hand, preferred stocks typically do not come with voting rights but offer shareholders priority when it comes to dividends and assets in case of liquidation.
Growth Stocks
Growth stocks are shares of companies that are expected to grow at a faster rate than the average market. These companies reinvest their earnings into expanding their business, rather than paying out dividends to shareholders. Investors are drawn to growth stocks for their potential for high returns, although they also come with higher risk due to their volatility.
Value Stocks
Value stocks are shares of companies that are considered undervalued by the market. These stocks are often priced lower than their intrinsic value, making them attractive to value investors. Value stocks typically have stable earnings, dividends, and lower price-to-earnings ratios. Investing in value stocks can offer potential for long-term growth and income.
Stock Market Indexes
Stock market indexes are tools used to measure and report the value of a specific section of the stock market. They provide investors with a general idea of how the market is performing overall. Major stock market indexes like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average are commonly used benchmarks to track the performance of the stock market.
Major Stock Market Indexes
- The S&P 500: This index tracks the performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is widely regarded as one of the best indicators of the overall health of the U.S. stock market.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA): This index consists of 30 large publicly traded companies in the United States, representing various sectors of the economy. It is one of the oldest and most widely followed indexes in the world.
Stock market indexes are calculated using a weighted average of the prices of the individual stocks included in the index. The weights assigned to each stock are based on factors such as market capitalization or price.
Calculation and Significance
Stock market indexes are calculated using different methodologies depending on the index. The significance of stock market indexes lies in their ability to provide investors with a snapshot of the overall market performance, allowing them to make informed investment decisions.
How to Buy Stocks

Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time, but it’s important to understand how to buy stocks before diving in. Here, we will discuss the steps involved in buying stocks, different methods of purchasing stocks, and factors to consider before making an investment.
Steps to Buy Stocks
- Open a brokerage account: Before you can buy stocks, you’ll need to open a brokerage account. This can be done through a traditional broker or an online platform.
- Research the stock: Before investing, research the company you’re interested in and analyze its financial health, performance, and future prospects.
- Choose the stock: Once you’ve done your research, select the stock you want to purchase based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Place an order: You can place an order to buy the stock through your broker or online platform. Make sure to specify the number of shares you want to buy and the price you’re willing to pay.
- Monitor your investment: After buying the stock, keep track of its performance and stay informed about any news or developments that may affect its price.
Methods of Purchasing Stocks
- Through a broker: Traditional brokers provide personalized investment advice and assistance in buying stocks, but may charge higher fees.
- Online platforms: Online brokerage platforms offer lower fees, convenient trading options, and access to research tools for independent investors.
Factors to Consider Before Investing, Stock Market Basics
- Financial goals: Determine your investment goals, whether it’s long-term growth, income generation, or capital preservation.
- Risk tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance and choose stocks that align with your comfort level for potential fluctuations in value.
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different stocks and sectors to reduce risk and maximize returns.
- Market conditions: Consider the overall market conditions and economic outlook before making investment decisions.
Risks and Rewards
Investing in the stock market comes with its own set of risks and rewards. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions when it comes to buying and selling stocks.
When it comes to risks, one of the main concerns is the volatility of the stock market. Prices can fluctuate rapidly, leading to potential losses if the market takes a downturn. Additionally, there is always a risk of losing your initial investment if a company fails or goes bankrupt. It’s important to be prepared for these possibilities and to diversify your portfolio to minimize risk.
On the other hand, investing in stocks can also bring significant rewards. One of the main benefits is the potential for high returns on your investment. If you choose the right stocks and the market performs well, you could see substantial gains over time. Moreover, investing in stocks allows you to participate in the growth of successful companies and industries, providing you with a stake in their success.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Stock Market Investments
- Successful Investment: Investing in tech companies like Apple or Amazon in their early stages and holding onto the stocks as they grew exponentially over the years. This resulted in significant returns for investors who had the foresight to invest early.
- Unsuccessful Investment: Investing in a company with a shaky financial foundation or a declining market position, leading to a sharp decline in stock prices. For example, investing in a company that eventually filed for bankruptcy, resulting in a total loss of investment.
